What are the molecular and cellular steps that govern presynaptic assembly and determine presynaptic function?
What is the order of assembly at nascent presynaptic specializations?
Visualizing presynaptic protein accumulation in the embryonic nerve ring over development.
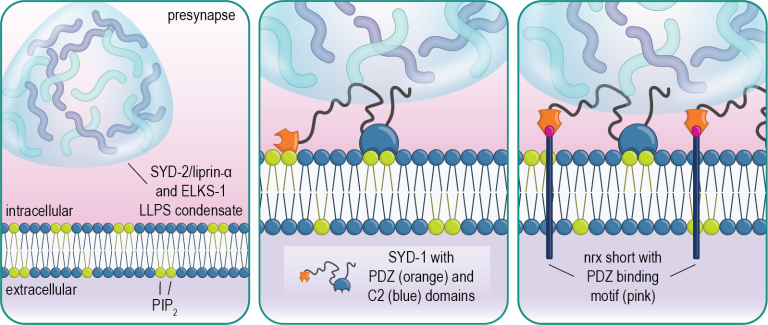
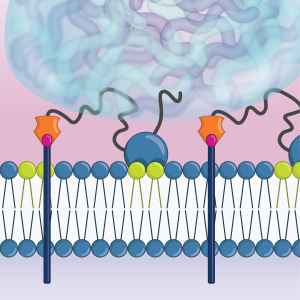
We have found that the presynaptic scaffold protein SYD-1 coordinates presynaptic assembly through interactions with phospholipids in the membrane including PIP2. SYD-1 then subsequently recruits the cell-adhesion molecule neurexin, which serves to stabilize these nascent assemblies (Frankel et al., 2025).
Molecular dynamics simulation of SYD-1’s C2 domain interacting with PIP2 (green) in the plasma membrane.
What is the role of Neurexin in presynaptic development?
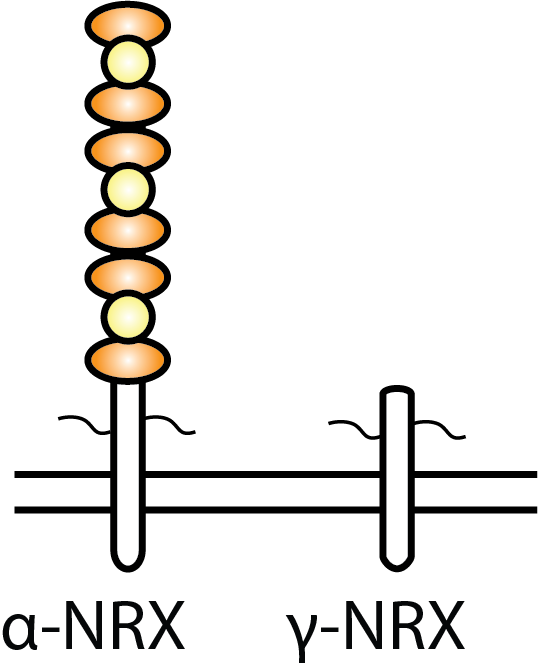
We have found that a short isoform of neurexin, called gamma neurexin,
which is conserved from worms to humans, is sufficient for mediating
presynaptic stabilization and maturation despite not containing any
extracellular binding domains.
Using proximity ligation (TurboID) and proteomics we found that the
intracellular domain of neurexin interacts with many actin-binding proteins
to mediate its function (Profes et al., 2024).
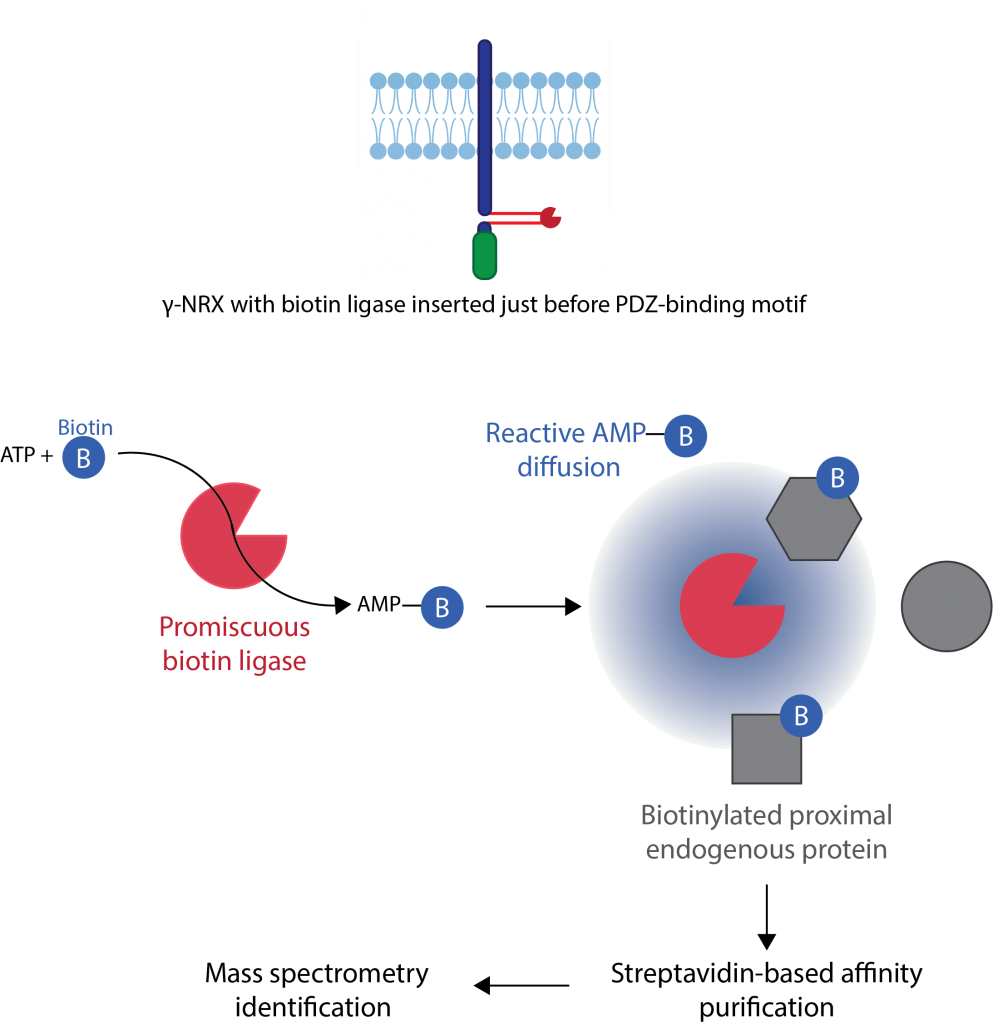
What is the role of presynaptic mRNAs in synapse development?
Beta-actin mRNA labeled using the MS2 system allows for the visualization of both transcription sites in the nucleus (brightest spots) and RNA granules inside and outside of the nucleus.
During axonal outgrowth, actin mRNA granules are transported towards the growth cone.
Non-canonical roles for cell adhesion molecules
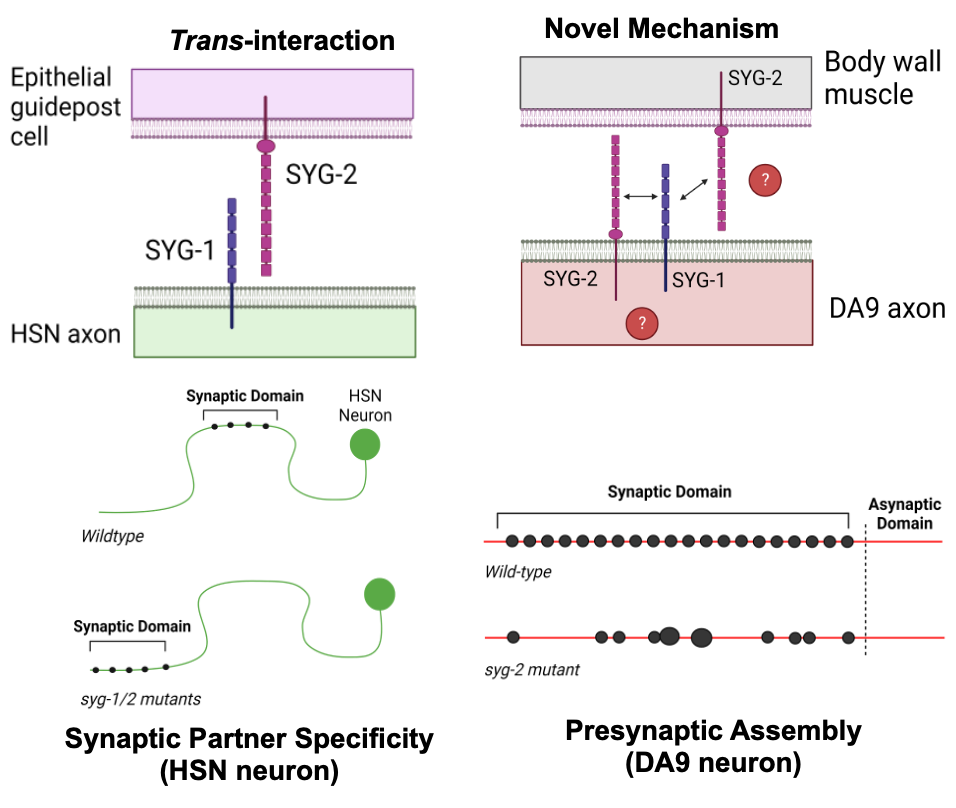
We have identified non-canonical roles in synapse assembly for a pair of CAMs, SYG-1 and SYG-2. We have found that both SYG-1 and SYG-2 are expressed and function in the same presynaptic cell, suggesting they may interact in cis, contrary to their previously described role in the C. elegans HSN neuron. Furthermore, we have found that the intracellular domain of SYG-2 alone is sufficient for inducing presynaptic assembly, in contrast to the accepted idea that the extracellular domains of CAMs are required for their function. Using CRISPR transgenesis, we can identify the critical sub-domains of SYG-1 and SYG-2 required for their function in presynaptic assembly.
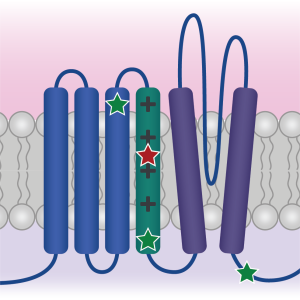
Characterizing human patient calcium channel variants in C. elegans
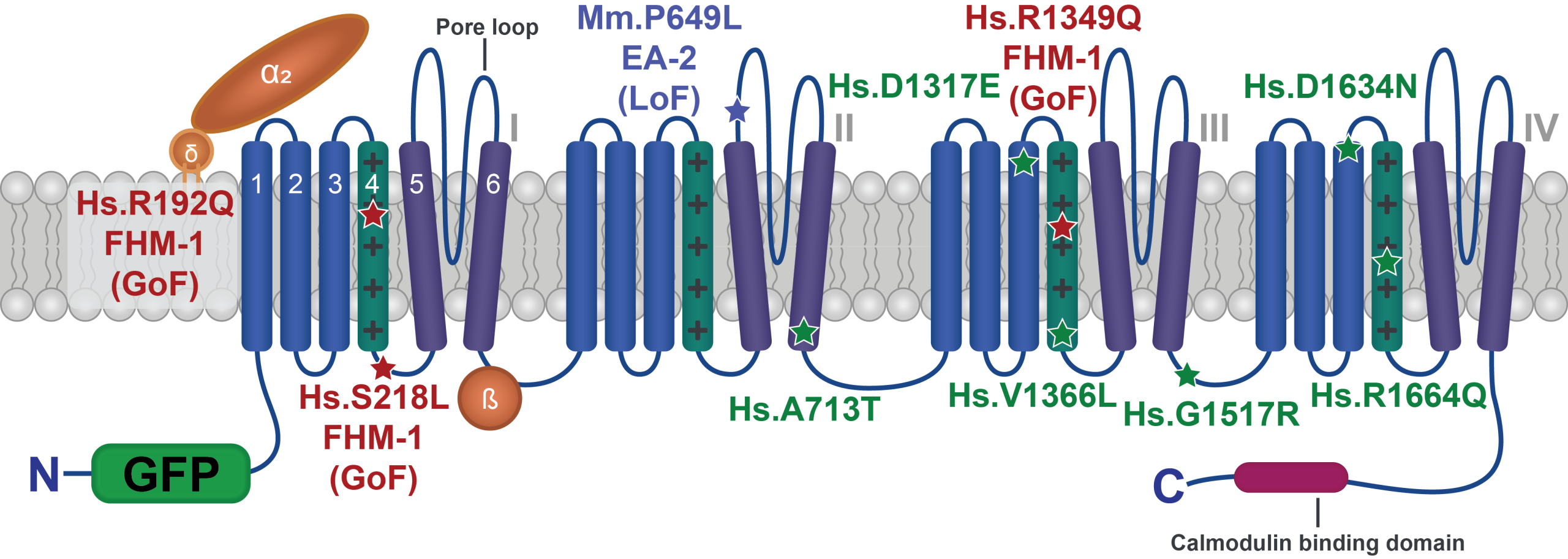
We are generating human patient variants in the CaV2-type voltage-gated calcium channel (encoded by the CACNA1A gene in humans) in the worm homolog (called UNC-2). Doing so enables us to understand the effect of these variants both on channel function and more broadly on synapse function, and may help explain why different variants in this single gene lead to such a diverse array of symptoms in patients.
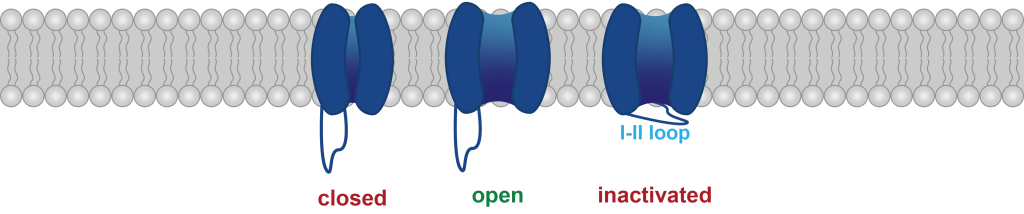
We are also examining how alternative splicing of these channels (particularly in intracellular loops that govern channel inactivation kinetics) might interact with patient-derived variants.
wild type
unc-2 mutant
Behavioral changes, such as an increase in “reversals” (or, backwards/forwards movement switches), are characteristic of some gain-of-function mutants in these channels. We can leverage this both to understand the circuit-level effects of these mutations as well as to perform forward genetic screens for suppressors of this phenotype, in the hopes of identifying additional therapeutic targets for patients with these variants.